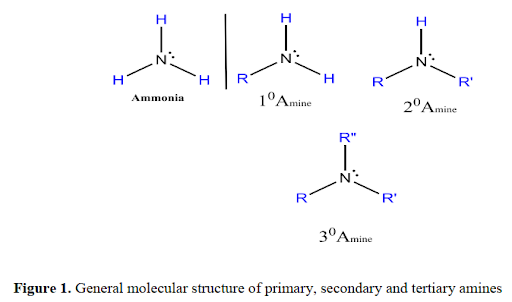
AMINE
Introduction:
Amines and amides are abundant in nature. They are a major component of
proteins and enzymes, nucleic acids, alkaloid drugs, etc. (Alkaloids are N containing,
weakly basic organic compounds; thousands of these substances are known.) Amines
are organic derivatives of ammonia (NH3), in which one or more of
the three H’s is replaced by a carbon group. Amines are classified as primary
(1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°), depending on how many carbon groups
are connected to the nitrogen atom, for example:
Nomenclature of Amines:
Primary, secondary and tertiary amines: common
names are obtained by alphabetically arranging the names of the alkyl
substituents on the nitrogen and adding the suffix -amine (e.g.,
ethylmethylamine).
Amines
in the IUPAC system: the “e” ending of the alkane name for the
longest chain is replaced with –amine.
The amine group is located by the position number. Groups that are attached to
the nitrogen atom are located using “N” as the position number. More complex
primary amines are named with —NH2 as the amino substituent.
Physical
properties of Amines:
1)
Phases: Lower
aliphatic amines (Liquid phase):
For
example: (a) CH3NH2 (Methylamine)
(b)
CH3CH2NH2
(Ethylamine)
•
If the amines having more than three hydrocarbon
alkyl chain amines which are liquid in nature because of increases the Van der
Waals force.
•
If the amines having 8 to 10 carbon atoms alkyl
chain amines which are solid in nature.
2)
Colour: In
case of aniline, it is colour less, but when it will come into contact in
atmosphere oxygen and convert into coloured form.
3) Solubility
in water: Water is a polar molecule
and amines having nitrogen groups in its molecular structure, so nitrogen is
electronegative in nature.
Electronegativity
order: F > O > N
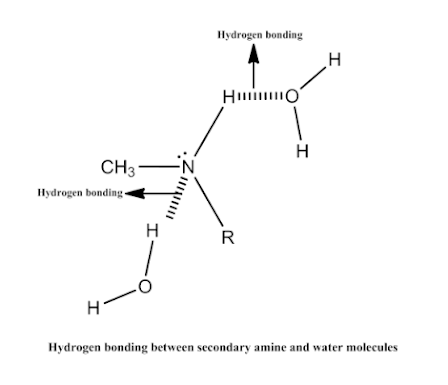
• Lower amines are soluble in water due to
formation of the hydrogen bonding.
• And higher carbon containing amines decreases
the solubility in the water.
• And amines are not soluble in the water due to increases the hydrophobicity of the amines.
1) Boiling
point:
CH3 CH2 CH2NH2
(Primary amine): It can form two-hydrogen bond form.
CH3CH2NH CH3 (Secondary
amine): It can form one-hydrogen bond form.
CH3)3N (Tertiary
amine): It cannot form any hydrogen bond form.
In Case, When the molecular formula
will same then the boiling point is follows as:
1°>2°>
> 3° Boiling point order
ROH > RNH2
> R2NH > R3N > R-H Boiling point oder
v
Primary
and secondary amines can hydrogen bond to each other:
v Intramolecular hydrogen bond possible in primary and secondary amines.
•
Tertiary amines cannot hydrogen bond to each other:
v Water Solubility: Primary
(1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) amines can all form hydrogen bonds with
water. Low-molecular weight amines are generally water soluble.
v Odour: Low molecular weight
amines tend to have sharp, penetrating odours similar to ammonia.
v Higher molecular weight amines often smell like
rotting fish, and are often found in decaying animal tissues.
Basicity of amines:
NOTE : Amines show strong
basicity as compared to the ammonia.
Order of the basicity of the amines primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary
(3°) amines
1) +I Effect:
+I Effect increases then basicity
of amines decreases, basic compounds are easily
donate the electrons pair.
Note: In the tertiary (3°) amines the three R groups donate the electron than in this situation
the electron density on nitrogen is increased and easily
donate the electron pair.
Tertiary amine > Secondary amine > Primary
amine: Basicity order of amine
Note: Tertiary amine > Secondary amine > Primary
amine: Basicity order of amine in the gas phase
2) Solvation theory (Applicable only for aqueous phase):
·
Compound having lower energy means it more
stable according to the law of thermodynamic.
v It means the three water molecules increases the stability as well as
decreases the energy of the molecules. So, the stability order follows as: primary
(1°) >Secondary
(2°) >Tertiary (3°).
3) Steric hindrance:
a) R = CH3CH2-
Note: Primary, secondary and tertiary amines show
different chemical reaction with the same reagent.
1)
Reactivity of amines:
v Due to acidic hydrogen and lone pair of amines at the nitrogen atom. Because of the lone pair they act as a base and nucleophile. Basic character of amines show due to lone pair of electron.
v In these reactions amines
act as a base. And all amines either primary, secondary or tertiary all are
showing this type of reactions.